
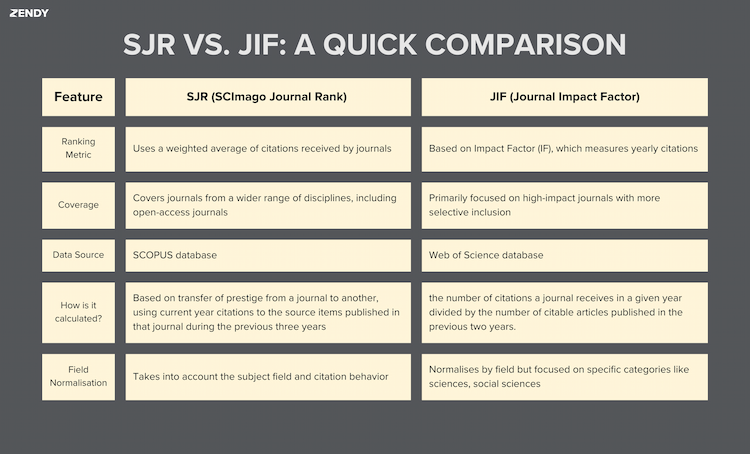
JIF vs. SJR Ranking: What's The Difference?
Two of the most common journal rankings are the Journal Impact Factor (JIF) and SCImago Journal Rank (SJR). They both measure journal impact but in different ways. Knowing how they work can help you choose the right journal to publish in. If you're deciding where to publish your research or assessing the significance of journals in your field, understanding these metrics can guide your choices. While both JIF and SJR aim to measure journal impact, they approach it differently. Depending on your needs, you might prefer one over the other or consider both for a well-rounded view. What Is SJR? Developed by SCImago using Scopus's database, SJR ranking evaluates the scientific impact of journals on their citations. Unlike a simple citation count, SJR assigns a higher value to citations from prestigious journals, meaning that not all citations carry the same weight. Key Features of SJR Ranking: Citation Quality Is Important: A journal's SJR ranking is influenced more by citations from reputable publications. Three-Year Citation Window: Citations are taken into account by SJR ranking for a duration of three years. Field-Normalised: SJR ranking takes into consideration variations among disciplines, which facilitates the comparison of publications from various fields of study. Open Access Inclusion: By incorporating open-access journals, SJR ranking provides a more comprehensive understanding of journal impact. What Is JIF? The Journal Impact Factor (JIF) provides one of the most well-known indicators of a journal, run by Clarivate and based on Web of Science database. Unlike SJR ranking, JIF is calculated by a straightforward ratio: the number of citations a journal receives in a given year divided by the number of citable articles published in the previous two years. Key Features of JIF: Two-Year Citation Window – Focuses on recent citations. Straightforward Calculation – It is simple to understand because it uses a simple average. Exclusive to Web of Science – Only Web of Science-indexed journals are included. Heavily Used in Academic Promotion – JIF is often a deciding factor in funding applications and tenure evaluations. Which Ranking Should You Use? It depends on what you're looking for. If you need a broader view of journal impact that considers citation prestige, SJR ranking may be more useful. If you're in a field where the Journal Impact Factor is commonly used for assessments (e.g., life sciences, medicine), JIF might be the better choice. If you're working with open-access journals, SJR provides a more inclusive perspective. In Conclusion While each ranking system has advantages, none of them is a perfect measurement of journal ranking quality. To have a better view of a journal's influence, think about examining a variety of classifications rather than depending solely on SJR ranking or JIF ranking. Knowing these distinctions will help you make well-informed choices, whether choosing a journal for publication or assessing a research paper. Sources: Clarivate Analytics Impact Factor SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) .wp-block-image img { max-width: 85% !important; margin-left: auto !important; margin-right: auto !important; }

Top 4 Challenges Every Researcher Has With Index Journals – And How To Solve Them
An index journal acts as a unique quality check for any academic research, however, it also comes with its unique challenges that even the most experienced researchers get disappointed. Starting with access issues to manoeuvring the virus of predatory journals, here are top 4 common problems researchers face when it comes to an index journal and actionable solutions. 1. Access Restrictions Yes, we are in 2025 and yet, access is still a problem. Many index journals are locked behind expensive paywalls, making it difficult for researchers to retrieve the articles they need. The Solution: Explore open-access options: Open-access libraries have many useful options that may be free or very inexpensive. Use platforms like Zendy: Using such platforms is a cost-effective option that can help researchers access infinite articles with ease. 2. Increased Research Time Looking for academic articles you need in an index journal can be a boring task with the huge volumes of publications to examine. The Solution: Use advanced search tools: Boolean queries and AI tools like ZAIA on Zendy can help improve results and save time. Set up alerts: Tools like Google Scholar can notify you about new publications in your field. Be mindful of DOI: A DOI (Digital Object Identifier) can be your best friend for quickly locating specific articles. Understanding how it works can simplify your research workflow. 3. Confusion Around Journal Indexing Not all indexed journals are reputable, and some low-grade journals claim to be worth considering. The Solution: Verify journal indexing: Use databases like Scopus or Web of Science to check a journal’s legitimacy. Avoid being a victim of fake journals: Predatory journals are a common trap for researchers. Read The Trap of Predatory Journals: How to Spot and Avoid Them for tips on how to spot and protect oneself from such journals. Seek expert advice: Consult mentors or colleagues to help you sort through confusing index journal lists. 4. Rejection of Manuscripts Rejection is a common challenge for researchers submitting manuscripts to indexed journals. The Solution: Focus on quality: With a little bit of effort on proofreading and formatting, the manuscript can make it easier to accept the submission. Learn about the importance of expert academic proofreading services for successful research to improve your submission. Consider alternative options: Rejections are part of the process. Explore other journals in your field and continue to improve the project. Conclusion Publishing in an index journal is important in the academic community, but the process can feel overwhelming at times. Using digital tools, learning how journal systems work, and exploring resources like those on Zendy can make the journey easier and more manageable for researchers. .wp-block-image img { max-width: 85% !important; margin-left: auto !important; margin-right: auto !important; }
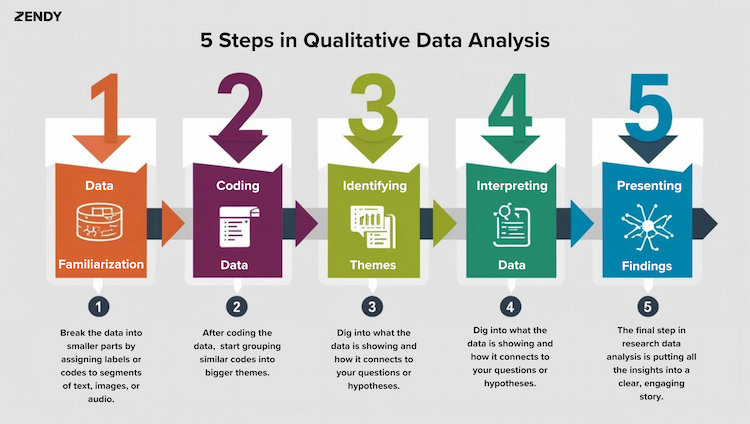
Qualitative Research Data Analysis: How Researchers Study Text, Images, and Audio
When researchers start collecting qualitative data, they work with non-number-based information such as interview scripts, images, or audio recordings. Analysing this kind of data might seem tough, however, qualitative data analysis gives us organised ways to understand detailed descriptive info. Let's look at how researchers address analytics in academic research for texts, images, and audio, while also talking about why research data analysis matters overall. What is Qualitative Data Analysis? Qualitative data analysis examines and interprets non-numerical data to understand underlying themes, patterns, or stories. Unlike quantitative analysis, which focuses on numbers and statistical relationships, qualitative analysis emphasises meaning, context, and subjective interpretation. This type of research data analysis is often used in fields like sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education. Steps in Qualitative Research Data Analysis 1. Data Familiarisation Before jumping into research data analysis, researchers take time to really get familiar with the data. They might read transcripts, examine images, or listen to audio recordings several times. The goal is to fully understand the content and its context. For example, a researcher looking at workplace communication might listen to recordings of team meetings to get a sense of the tone, how the conversation flows, and the main topics being discussed. 2. Coding the Data Coding is a fundamental step in research data analysis. Researchers break the data into smaller parts by assigning labels or codes to segments of text, images, or audio. These codes represent themes, ideas, or categories that emerge from the data. 3. Identifying Themes After coding the data, researchers start grouping similar codes into bigger themes. These themes are the main ideas or patterns that help answer the research question. 4. Interpreting the Data Interpretation in research data analysis is about making sense of the themes in light of the research goals. Researchers dig into what the data is showing and how it connects to their questions or hypotheses. 5. Presenting Findings The final step in research data analysis is putting all the insights into a clear, engaging story. This often involves using quotes from participants, highlighted images, or excerpts from audio transcripts to back up the findings. Tools for Qualitative Data Analysis While many researchers still analyze data manually, software tools can make the process a lot easier. Softwares like NVivo, ATLAS.ti, and MAXQDA help with coding, organising, and visualising the data. These tools are especially helpful in research data analysis when working with large datasets. Applications of Qualitative Data Analysis 1. Text Analysis Textual data includes interview transcripts, written surveys, and documents. Researchers examine word choice, sentence structure, and overall content to uncover insights. 2. Image Analysis Analysing images in research data analysis involves looking at visual elements like colour, composition, and symbolism. This is often used in media studies, art history, and cultural research. 3. Audio Analysis Audio data analysis in research, such as recorded interviews or podcasts, requires careful listening to capture nuances like tone, emphasis, and pauses. The Importance of Data Analysis in Research Qualitative data analysis is a vital part of research, it helps to uncover the stories and meanings behind the numbers. It gives context and depth to numerical data. By working with non-numerical data researchers can: Understand how people think and behave in different situations Explore cultural and social trends to see how they shape communities. Build theories based on real-life experiences and observations Qualitative Research Best Practices 1. Be Clear About Your Purpose Start with a straightforward question or goal. Why are you conducting this research? Knowing what you're looking for helps you stay focused and avoid getting lost in the details when conducting research data analysis. 2. Choose the Right People Who can give you the best insights? Look for a mix of people with different experiences or perspectives. That makes it more valuable. 3. Build a Comfortable Environment Imagine yourself as one of the participants. Would you be at ease expressing your opinions in this setting? People are more open in an informal, welcoming environment. 4. Keep an Open Mind The unexpected may lead to the most insightful discoveries. Be adaptable and curious; go with the flow of the discussion. 5. Pay Attention to the Details Make thorough notes or, with consent, record the conversation. A person's tone, pauses, and body language can all give away a lot about their intentions. 6. Treat People with Care Be mindful of participants' boundaries, privacy, and time. Make sure they understand how their contributions will be used and that their contributions are valued. 7. Organise Your Findings Sort your data into themes or patterns once you have it. Look for frequent arguments people give when answering your question. 8. Share What You Learn Use actual quotes or cases as you write up your findings so that readers may see what others are saying in their own words. 9. Keep Learning Each project is an opportunity to develop your abilities. To improve even more over time, take note of what went well and what didn't. In conclusion Research data analysis in qualitative studies turns raw data into insights. Whether it’s text, images or audio this process helps researchers explore the personal and cultural aspects of their work, to gain a deeper understanding of the experiences and views behind the data. It combines structure with interpretation to make rich descriptive data meaningful. .wp-block-image img { max-width: 85% !important; margin-left: auto !important; margin-right: auto !important; }
Science Citation Index vs. Scopus: Which Database is Right for You?
The Science Citation Index (SCI) and the Scopus database are two of the most widely used citation indexing systems in academic research. Researchers, institutions, and funding bodies rely on these databases to evaluate research impact, track citations, and facilitate collaborations. But how do they compare? And which one should you use for your research? Who Founded Science Citation Index? The Science Citation Index (SCI) was introduced in 1964 by Dr. Eugene Garfield to track the flow of scientific ideas through citations. Started as a print-based resource, it later evolved into a digital database, now integrated into the Web of Science. Over the years, SCI made a huge impact on research careers, helping researchers assess the academic influence of scientific papers based on citation data. A Brief History of the Scopus Database In the early 2000s, competing databases featuring citation statistics were introduced, the most notable being Scopus, launched in 2004. The Scopus database, launched by Elsevier, provides a broader multidisciplinary citation index. Unlike the Science Citation Index, which traditionally focused on leading science journals, Scopus includes publications from a wider range of disciplines, including the social sciences, humanities, and technical fields. What is the Difference Between Science Citation Index and Scopus Database FeatureScience Citation IndexScopusPublisherPart of Clarivate’s Web of Science platform.Managed by Elsevier.Scope and SizeFocuses primarily on high-impact scientific journals.Covers a broader range of disciplines. (social sciences, humanities, and conference proceedings)Regional RepresentationHas a more selective approach.Includes journals from diverse regions, including non-English publications.Tools and MetricsFocuses on traditional citation counts, traditional citation counts and h-index.Offers advanced metrics like SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) and SNIP.To know the difference between h-index, SNIP, and Impact Factor, read our recent blog about the Journal's Classification Systems. Why is Science Citation Index important? The Science Citation Index (SCI) is a critical database for evaluating scholarly reputation and research impact, particularly in scientific fields. Inclusion in SCI is often seen as a mark of prestige, as it only indexes top-tier, high-impact journals. This gives credibility to both the research published within these journals and the researchers themselves. Also, the Impact Factor derived from SCI data is one of the most respected metrics for assessing the significance of research articles and journals How Science Citation Index Helps Researchers: Tracking Research Impact Finding Relevant Literature Facilitating Collaborations Why is Scopus important? Scopus is a key database for you as a researcher looking to stay on top of your field. It helps you track citation trends, see which studies are getting the most attention, and figure out where to focus your publication efforts. Researchers use it to get a clear picture of how their work fits into the broader conversation and which areas are generating the most interest. Scopus also includes a wider range of high impact journals and additional metrics like SJR and SNIP, which could be valuable for certain types of research, especially interdisciplinary or emerging fields. How Scopus Database Supports Researchers: Broader Coverage Additional Metrics Regional Inclusion Should You use Scopus or Science Citation Index? Use Scopus if you need broader coverage, especially across interdisciplinary fields, or if you're interested in tracking newer trends and conference papers. Use SCI if you prioritise high-quality, curated content with a focus on traditional scholarly disciplines and need detailed citation metrics like the Impact Factor. Conclusion Both the Science Citation Index and the Scopus are essential citation databases for academic research, each with its strengths and limitations. The best choice depends on your research needs—whether you prioritise broad coverage (Scopus) or deep focus (SCI). As citation databases continue to evolve, the focus will remain on improving accuracy, accessibility, and fairness in academic evaluation. .wp-block-image img { max-width: 85% !important; margin-left: auto !important; margin-right: auto !important; }
International Day of Education, AI and education: Preserving human agency in a world of automation
Every year on January 24, people around the world come together to celebrate the International Day of Education. It’s a time to reflect on how AI in education shapes our lives, opens up opportunities, and helps build more knowledge and discoveries. For 2025, the theme is both timely and thought-provoking: "AI and Education: Preserving Human Agency in a World of Automation." The 2025 theme highlights the growing role of artificial intelligence (AI) in education. It’s about exploring how learning can help us navigate new technology while making sure we stay in charge of the decisions and ideas that shape our future. With automation becoming more common, the conversation focuses on how we can balance these advances with our values and individuality while using AI responsibly. What’s Happening This Year? UNESCO will host a gathering at the United Nations headquarters to explore the relationship between AI and education, focusing on how education can adapt to these changes and exploring its opportunities and challenges Global Event in Paris: On January 24, 2025, UNESCO will host a global event in Paris focusing on the intersection of AI and education. Global Event in New York: A parallel event will take place at the United Nations headquarters in New York, addressing similar themes. Webinar on Lifelong Learning in the Age of AI: Organised by the UNESCO Institute for Lifelong Learning, this online webinar on January 24, 2025, will explore the implications of AI for lifelong learning. Why This Day Matters The International Day of Education is a reminder of how essential learning is to solving big challenges, such as poverty, climate change, inequality, conflict, public health, and access to resources. It’s a moment to share progress, build connections, and spark new ideas for making education better and more inclusive. By focusing on AI this year, the goal is to encourage thoughtful discussions about how technology can work for us without losing sight of what makes us human. Read More .wp-block-image img { max-width: 85% !important; margin-left: auto !important; margin-right: auto !important; }
Address
John Eccles HouseRobert Robinson Avenue,
Oxford Science Park, Oxford
OX4 4GP, United Kingdom
