
The Journal of Financial Economics
A top peer-reviewed journal since 1974 published by Elsevier, founded by Michael C. Jensen, Eugene Fama, and Robert C. Merton. The Journal of Financial Economics (JEF) serves as a dedicated platform for publishing high-quality studies on financial markets, corporate finance, financial intermediation, entrepreneurial finance, corporate governance, organisational economics, macro-finance, behavioural finance, and household finance. Focused on both theoretical and empirical research in financial economics. The Journal of Financial Economics prioritises rigorous empirical, theoretical, and experimental contributions, particularly those related to the theory of the firm and financial economics. Journal of Financial Economics Impact Factor and Rankings According to the latest updates from VU Journal Publishing Guide, The Journal of Financial Economics has made a big impact, with an impressive 10.4 impact factor as of 2024. That puts it among the top economics and finance journals globally. It ranks 5th out of 600 in the Economics category and takes the top spot—1st out of 233—in Business, Finance. These rankings highlight just how influential the journal is in its field. AbbreviationJ. FINANC. ECONISSN0304-405X (1879-2774)eISSN:N/ACategoryAccounting (Q1); Economics and Econometrics (Q1); Finance (Q1); Strategy and Management (Q1)WoS Core Citation IndexesSSCI - Social Sciences Citation IndexJournal Impact Factor (JIF)10.45-year Impact Factor11.4Best ranking:ECONOMICS (Q1) Percentage rank: 99.2%CountrySWITZERLANDPublisherElsevier Source: WoS Journal of Financial Economics Scopus Metrics According to Scopus data for 2023, the journal's metrics are equally impressive: SCImago Journal Rank (SJR): 13.655 Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP): 5.048 CiteScore: 15.8 These metrics reinforce the journal's reputation as a leader in its field, with high rankings in many categories including Accounting, Finance, Economics and Econometrics, and Strategy and Management. Journal of Financial Economics H-index and Citations The Journal of Financial Economics has an exceptional h-index of 311, indicating that at least 311 articles published in the journal have been cited at least 311 times each. This high h-index reflects the journal's strong impact and the enduring relevance of its published research. What is The Scope of The Journal of Financial Economics? The journal covers a wide range of topics within finance and economics, including: Accounting Economics and Econometrics Finance Strategy and Management It's particularly known for its applied papers and case studies section, which provides a platform for scholarly studies of actual cases, events, or practices in the financial world. Conclusion The Journal of Financial Economics stands out as a top-tier publication in its field, consistently ranking highly across various metrics. Its high impact factor, impressive SJR, and strong h-index all point to its significant influence in the world of financial economics. For researchers and professionals in finance and economics, publishing or referencing articles from this journal can lend considerable weight to their work. .wp-block-image img { max-width: 85% !important; margin-left: auto !important; margin-right: auto !important; }

We Are Exhibiting UKSG 2025 Annual Conference & Exhibition in Brighton!
We're thrilled to announce that we will be exhibiting at the 48th UKSG Conference from March 31 to April 2, 2025, in Brighton, UK. Visit us at booth #79 to experience: Live Demonstrations: See how Zendy’s AI-powered tools, like ZAIA and AI Summarisation, can streamline your research with reference-backed answers to all your research questions and concise summaries of complex academic papers Personalised Consultations: Meet our team to discuss how Zendy can support your library’s digital transformation. Interactive Sessions: Learn about our affordable subscription models and global accessibility initiatives. Meet Kamran Kardan, Sara Crowley Vigneau and Lisette van Kessel to learn how Zendy is making knowledge more accessible and affordable for researchers, students, and professionals worldwide. Don't miss this opportunity to explore the future of scholarly communication. To schedule a meeting with our team, please email us at info@zendy.io About UKSG Annual Conference: The UKSG Conference is a premier event in scholarly communications, attracting global delegates including librarians, publishers, researchers, and students. It offers an excellent platform for networking and exploring the latest trends in the research and publishing community. To learn more visit: https://www.uksg.org/events/conference25/ .wp-block-image img { max-width: 50% !important; margin-left: auto !important; margin-right: auto !important; }

We are Attending the 20th Annual Electronic Resources & Libraries (ER&L) Conference
We’re excited to announce that we will be attending the 20th Annual Electronic Resources & Libraries (ER&L) Conference from March 23–26, 2025, in Austin, Texas! This milestone event brings together professionals in e-resources, digital services, and the library industry to share insights, foster innovation, and build connections. Let’s Connect! If you’re attending ER&L 2025 or will be in Austin during the event, set up and schedule a meeting with our Co-founder Kamran Kardan. Please email us at info@zendy.io to schedule a time to discuss ZAIA’s vision for the future of AI in research and digital innovation. About ER&L 2025 The ER&L Conference is a community-driven event celebrating its 20th year of bringing together professionals passionate about electronic resources and digital services. With a peer-reviewed program shaped by industry experts, it’s the perfect space to explore trends, technologies, and solutions shaping the future of libraries. Location: Austin, USADates: March 23–26, 2025 Join us as we celebrate two decades of innovation in e-resources management! We look forward to seeing you there! To learn more visit – https://electroniclibrarian.org .wp-block-image img { max-width: 85% !important; margin-left: auto !important; margin-right: auto !important; }

Announcing our RAG-Based Revenue-Sharing Model for Academic Publishers
We are excited to announce a first-of-its-kind revenue-sharing model for AI-generated content, ensuring that publishers are fairly compensated when their paywalled research is cited by AI. Zendy Co-founder Kamran Kardan Our domain-specific large language model (LLM), ZAIA, uses Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to retrieve data from a diverse collection of open access (OA) and paywalled metadata through licensing agreements with publishers. Based on reference generation by the LLM, our new revenue-sharing model enables a fair and sustainable approach to compensating academic publishers for the use of their content by AI. Empowering Publishers with AI Innovation For years, major academic publishers have been cautious about AI companies using their research, citing copyright concerns, revenue impact, and the need for proper attribution. Our new model introduces a transparent, ethical approach for publishers to monetise their content in the AI era. Many large language models are restricted to training on publicly available research, as major publishers have not yet actively licensed their work to AI companies. Our revenue-sharing model is one of the first of its kind, ensuring clear consent, proper attribution, and fair compensation based on content retrieval. The transparent revenue-sharing mechanism ensures fair compensation for publishers based on the number of references provided in ZAIA’s responses. Our co-founder, Kamran Kardan, said: "This is a positive shift for the academic publishing industry. For the first time, AI is being used to drive revenue back to publishers instead of bypassing them. Ethical AI also means giving credit—and compensation—where it’s due. In the long term, we believe even authors should share in this revenue." We are partnering with a range of international publishers on this model, including IT Governance, Lexxion, British Online Archives, and Lived Places Publishing. Additionally, the RAG model is available for open access publishers, and we are currently exploring alternative compensation models for open access. A Leap Forward for Researchers and Institutions ZAIA provides users with precise, contextually relevant content tailored to their research needs. It offers answers to researchers' questions with reference-backed responses, ensuring that researchers and institutions can access high-quality, peer-reviewed materials while supporting the publishers who produce them. Promoting Sustainable and Ethical AI Content Partnerships To deliver accurate, unbiased, and comprehensive insights, large language models (LLMs) require diverse academic content. Our RAG-based model encourages broader collaboration between publishers and AI companies, fostering ethical agreements rooted in mutual licensing. Direct licensing with publishers allows us to guarantee high-quality, accurate, and up-to-date content, including retractions and data updates, thereby placing research integrity at the heart of our platform and our development of sustainable AI. We invite publishers, researchers, and institutions to collaborate in shaping the future of AI-driven research. To learn more about partnership opportunities, visit www.zendy.io or contact us at partnerships@zendy.io. About Zendy We are an AI-powered research library with over 780,000 users across 190+ countries. Designed to streamline the research process, we provide access to millions of journals, articles, and e-books, while offering a range of AI-driven tools, including ZAIA, an AI assistant that helps researchers expedite their research journey. We collaborate with leading academic publishers to make scholarly content more accessible and affordable, ensuring that users can explore high-quality research with ease. Zendy was created to facilitate access to academic literature. By addressing the key challenges that researchers face with traditional ways of finding relevant, high-quality academic content, we strive to provide peace of mind to students, researchers, professionals, and knowledge enthusiasts. We are developed by Knowledge E in a growing collaboration with researchers, students, institutions, and publishers. Our mission is to democratise access to content by making it more affordable and accessible. There are no limitations on reading, just simple access to scholarly resources. For more information visit zendy.io. .wp-block-image img { max-width: 85% !important; margin-left: auto !important; margin-right: auto !important; }
How to Find Peer-Reviewed Articles for Your Research
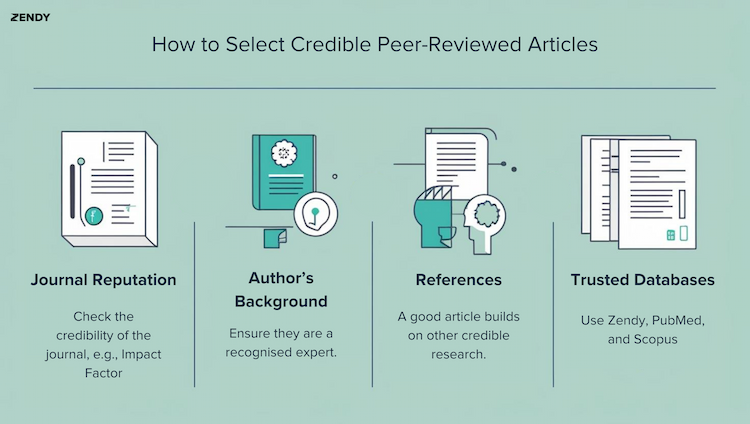
If you're doing research, you'll want to use reliable sources. Peer-reviewed articles are among the best because experts review them before they're published, ensuring quality and credibility. The benefits of expert peer review in research are significant—it helps maintain high standards, validates findings, and improves the overall reliability of academic work. But how do you find these peer-reviewed journal articles, and how can you tell if a journal is peer-reviewed? Let's break it down. What Are Peer-Reviewed Articles? A peer-reviewed article is one that has been checked by other experts in the field before publication. This process helps make sure the research is solid and trustworthy. Where Can You Find Peer-Reviewed Journal Articles? You can find peer-reviewed articles in a few different places: University Libraries – If you're a student or faculty member, your university library probably gives you access to research databases. Academic Databases – Websites like PubMed, JSTOR, ScienceDirect, and Web of Science have collections of scholarly peer-reviewed articles. Zendy – Affordable and accessible peer-reviewed scholarly content, in partnerships with leading publishers e.g., IntechOpen, IEEE, IT Governance Publishing, and IGI Global, powered by AI. Google Scholar – Some journal articles here are peer-reviewed, but not all. You’ll need to check the source. See The Growth of Digital Libraries: Benefits, Challenges & Trajectory How to Recognise Peer-Reviewed Journal Articles There are 4 ways to check if a journal is peer-reviewed or not: Visit the Journal’s Website – Look for a section about their review process. Use Library Databases – Many academic databases label peer-reviewed journals. Check the Editorial Board – A peer-reviewed journal usually lists experts who review submissions. Look It Up on Ulrichsweb – This directory can tell you if a journal is peer-reviewed. Are Google Scholar Articles Peer-Reviewed? Not necessarily. Google Scholar collects all sorts of academic work, including conference papers and preprints, which may not have gone through peer review. To check, see if the article was published in a reputable journal. What Is a Peer Review Example? Let’s say a scientist submits a research paper to a journal. The editor sends it to other experts, who review it for accuracy and clarity. And then they might suggest changes or reject the paper if it doesn’t meet the journal’s standards. So if the paper gets approved, it’s published as a peer-reviewed article. What’s the Difference Between Peer Review and an Original Article? Peer Review – A process where experts evaluate a research paper before it’s published. Original Article – A research paper that presents new findings. Some original articles are peer-reviewed, while others aren’t. How To Select Peer-Reviewed Journal Articles? When looking for peer-reviewed articles: Check the Journal – Make sure it's known for publishing peer-reviewed articles. Look at the Author’s Background – Are they an expert in the field? Review the References – Good research builds on other credible studies. Use Trusted Databases – Databases like Zendy, PubMed, and Scopus focus on peer-reviewed work. How Do You Know If a Peer-Reviewed Article Is Credible? Even among scholarly peer-reviewed journals, some are more reliable than others. Here’s what to look for: Reputation of the Journal – Some journals have stricter standards than others. Possible Bias – If a study is funded by a company with an interest in the results, for example, a pharmaceutical company funding a study on its own medication might have an interest in positive findings, be cautious. Strong Research Methods – A reliable, peer-reviewed article clearly explains how the research was conducted and how conclusions were reached. Retraction History – Some papers are later retracted due to mistakes or misconduct. Check if the article has been retracted. Final Thoughts It’s not hard to find peer-reviewed journal articles; it just takes a trusted source and a clear understanding of what you’re looking for. Digital libraries like Zendy give you access to everything you need in one place, including both free and paywalled peer-reviewed articles, with over 40 million articles across disciplines like engineering, medicine, economics, and more. .wp-block-image img { max-width: 85% !important; margin-left: auto !important; margin-right: auto !important; }
Address
John Eccles HouseRobert Robinson Avenue,
Oxford Science Park, Oxford
OX4 4GP, United Kingdom
